When most of humanity was confined due to the Coronavirus pandemic, we inaugurated a new Hope with respect to nature: the forests seemed to expand and the skies cleared at the same rate that the highways emptied, and few still forget the images of wild boars walking through the streets of Barcelona, or those of bears doing the same in Asturias .
However, those months of relief for our ecosystems they do not seem to have been enough for the air we breathe to have substantially improved if we take into account the whole of 2020. This is confirmed by the World Air Quality Report study recently published by IQAir, a Swiss company dedicated to controlling air quality in the world from tens of thousands of sensors located in 5,000 cities in 106 different countries.
"The COVID-19 pandemic was a major and one-off factor influencing air quality during 2020 . Some called it the 'largest-scale experiment ever conducted' on air quality. The temporary reduction in fossil fuel consumption caused by lockdowns around the world was correlated with significant declines in air pollution compared to previous years. In 2020, a remarkable 65% of global cities experienced improvements in air quality compared to 2019, while 84% of countries saw improvements overall . Due to the circumstances of these improvements, pollutant concentrations are likely to return to their usual levels," the study read.
"Unfortunately, 2020 also witnessed several extreme air pollution events in the form of forest fires and dust storms related to rising global temperatures as part of climate change and agricultural practices. Unprecedented wildfires devastated the United States, Australia, Siberia and South America, while Indonesia and parts of Africa also experienced devastating agricultural fires. These events resulted in significant spikes in air pollution in these areas, while also they emitted copious amounts of greenhouse gases . While continuing contributions to global air pollution come from burning of fossil fuels and industrialization , the mutual benefits of tackling those who contribute to both climate change and air pollution are becoming more apparent," the report continues.
In this way, while large cities such as Singapore (-25%), Beijing (-23%) and Bangkok (-20%) saw the largest reductions in PM2.5 emissions of the sample, others like São Paulo (+5%), Los Angeles (+1%) and Melbourne (+1%) saw the largest increases in PM2.5 compared to 2019 levels. "All three were affected by severe forest fire seasons, which greatly affected annual PM2," they explain from IQAir.
WHAT IS PM2.5 AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT?
Among the pollutants that are commonly measured to measure air quality, it is understood that fine particles (PM2.5) are the most harmful to humans due to their prevalence and high health risks . Thus, exposure to PM2.5 has been related to the appearance of cardiovascular diseases, respiratory diseases, premature mortality, asthma, lung cancer, low birth weight and stroke . New studies also claim that it is related to mental health disorders, Alzheimer's and vision loss.
These particles include a wide variety of chemical compounds and come from several different sources. The most common man-made sources include fossil fuel-powered motor vehicles, power generation, industrial activity, agriculture, and biomass burning.
"More than 90% of the world's population breathes dangerously high levels of air pollution . Due to its ubiquity and severity, Air pollution is the world's greatest environmental health hazard. , and contributes to up to seven million premature deaths worldwide per year (three times more than the deaths associated with Covid-19)," they explain from the Swiss company. Likewise, air pollution also wastes more than five billion dollars per year (4.18 billion euros).
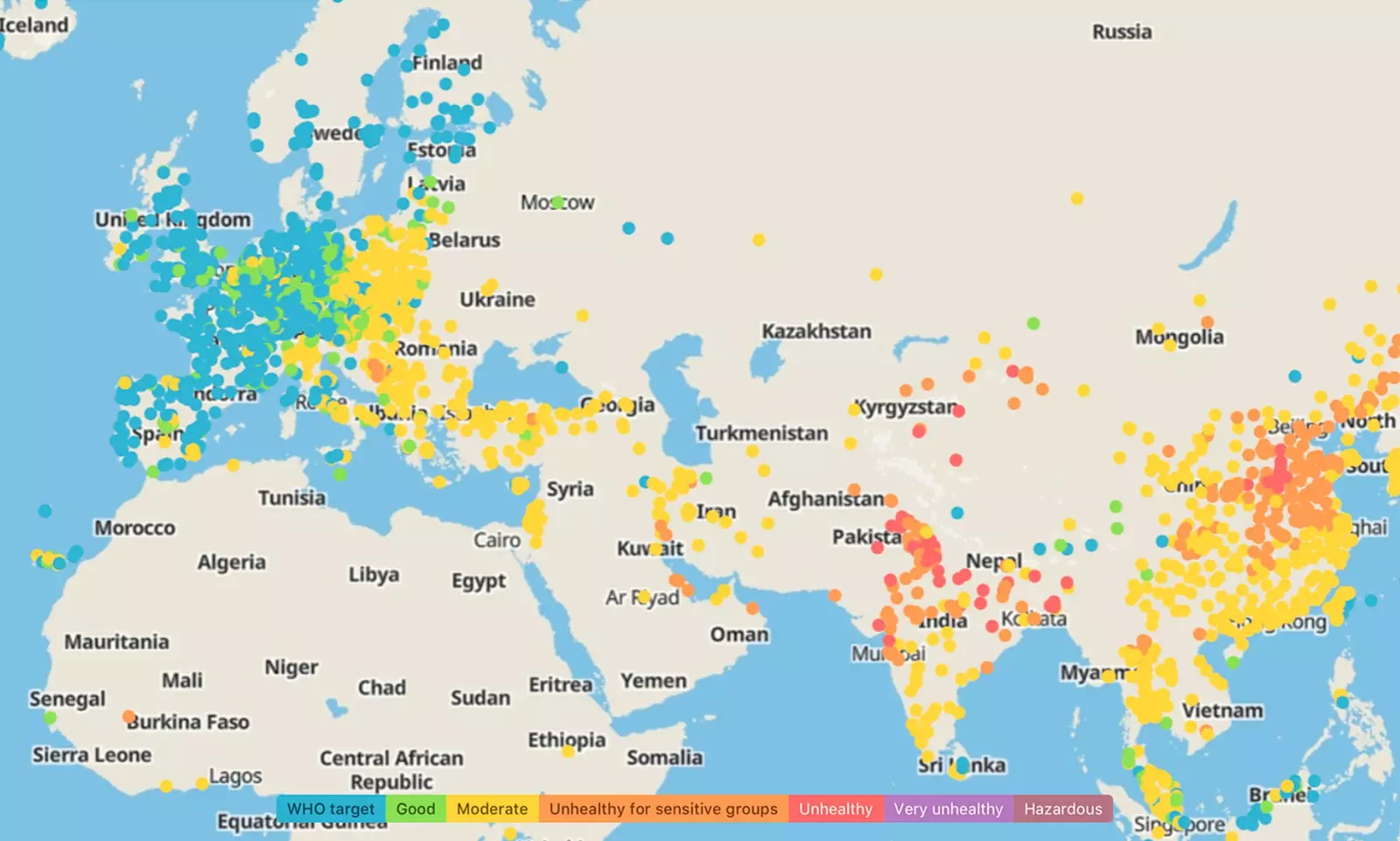
WORLD AIR QUALITY ON A SINGLE INTERACTIVE MAP
IQAir has enabled a map on its website where you can see, interactively, the results of its PM2.5 measurement in 2020 by region. In Spain, for example, it can be seen that places like Madrid, Murcia, A Coruña or Bilbao , among other cities on the north coast of the country, are at a good to moderate level of exposure to PM2.5 particles. The excellent thing is to reach the WHO objective -celestial points-, established by the European Union as the minimum admitted to be able to preserve human health. This fixes its mean annual value cannot exceed 10 micrograms per cubic meter , a level that, in any case, does not guarantee the safety of the air.
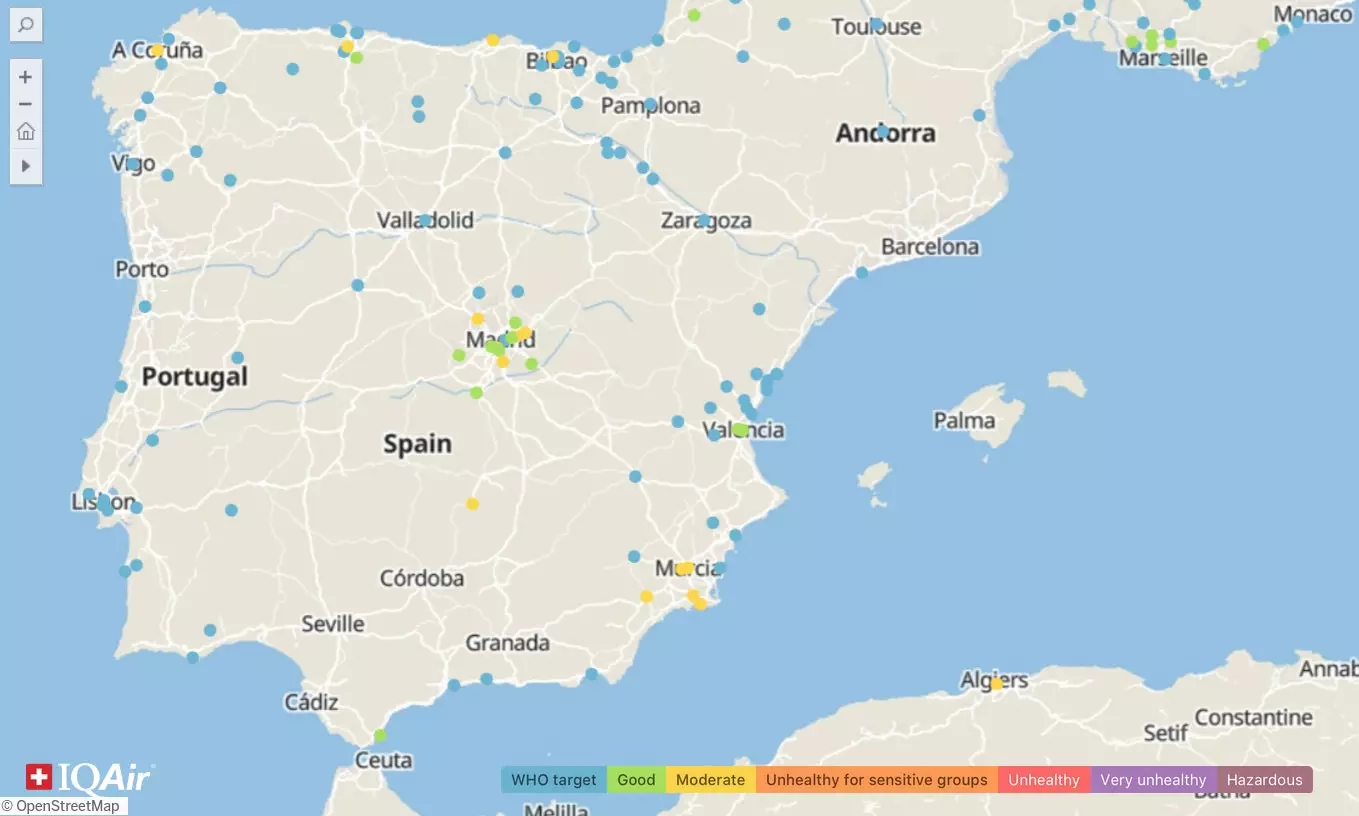
The air is of poorer quality in the enclaves with yellow dots: Madrid, Murcia, A Coruña, Bilbao...
In sum, The country with the highest concentration of PM2.5 in the world is Bangladesh. (77.1 µg/m³), followed by Pakistan (59), India (51.9), Mongolia (46.6), and Afghanistan (46.5). In Europe, it is Bulgaria the State that occupies the first position (27.5 µg/m³), followed by Serbia (24.3). Spain is in the 80th position among the 106 countries studied, with an average of 10.4 µg/m³ per year, while the place that holds the record in best air quality in the world is Puerto Rico , followed by New Caledonia, the Virgin Islands, Sweden and Finland.
WHAT CAN WE DO TO LOWER THESE ATMOSPHERIC POLLUTION LEVELS?
From IQAir they encourage governments to reduce emissions betting on renewable energy in all types of processes and vehicles. They also propose to establish harsher punishments companies that do not meet the required emission standards.
In the case of people, what can be done to preserve health is reduce exposure to pollution reducing the intake of outside air and wearing anti-pollution masks when atmospheric reading appear dangerous. Likewise, in order not to contribute to global pollution, they encourage us to choose clean modes of transportation and reduce energy and waste spending whenever possible.
